|
In this project, we investigate the problem of visibility-based target tracking for a team of mobile observers trying to track a team of mobile targets. We consider the tracking strategies for a general environment including the presence of obstacles. Finally, the strategies presented accommodate an arbitrary number of observers or targets.
|
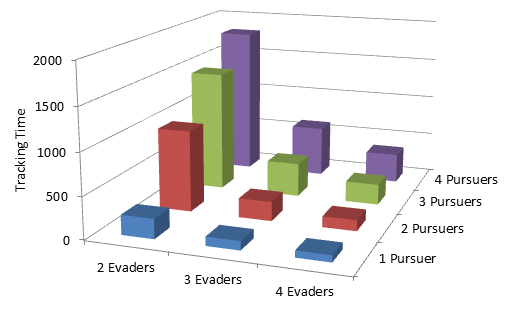
In this paper, we address the problem of visibility-based target tracking for a team of mobile observers trying to track a team of mobile targets. Based on the results of previous work, the notion of pursuit fields around a single corner is introduced. We use the pursuit fields to generate navigation strategies for a single observer to track a single target in general environments. In order to tackle the case when more than one observer or target is present in the environment, we propose a two level hierarchical approach. At the upper level, the team of observers use a ranking and aggregation technique for allocating each target to an observer. At the lower level, each observer computes its navigation strategy based on the results of the single observer-single target problem, thereby, decomposing a large multi-agent problem into several 2-agent problems. Finally, we present a scalable algorithm that can accommodate an arbitrary number of observers and targets. The performance of this algorithm is evaluated based on simulation and implementation.
M. Zhang and S. Bhattacharya,
Multi-agent Visibility Based Target Tracking Game. In
International Symposium on Distributed Autonomous Robotic Systems, Pages 440-451, 2014.
|
|
In this paper, we address the problem of decentralized visibility-based target tracking for a team of mobile observers trying to track a team of mobile targets. Based on the results of previous work, we extend this problem to the scenario when multiple observers and targets with incomplete communication graph are present. We propose a two level hierarchical approach. At the upper level, each observer is allocated to a target through a local minimum cost matching. At the lower level, each observer computes its navigation strategy based on the results of the single observer-single target problem, thereby, decomposing a large multi-agent problem into several 2-agent problems. Finally, we evaluate the performance of the proposed strategy in simulations and experiments.
R. Zou and S. Bhattacharya,
Visibility based multi-agent surveillance strategies in decentralized network. In
Proc. SPIE, pp. 94640P-94640P-6, 2015.
|
|
